http://www.doctorhousingbubble.com/housing-affordability-17-us-markets-near-potential-price-bottoms-socal-midtier-housing-real-estate-prices/
The list varies across the country. I’ve included a handful of California markets as well. In these areas if you have secure employment and would like to settle down, there is likely to be very little reason not to buy. This isn’t a question of being a bear or a bull. It is a question about understanding home values in a historical and local context.
Housing affordability matters. One of the biggest line items used to qualify home buyers is yourhousehold income. This is why it is hard to understand why some people simply choose to ignore the most important factor in sustaining housing markets. Household income drives rental prices and also drives household values historically. Should these ratios get out of whack because of exotic mortgages or imprudent lending then prices will rise but as we are seeing, will adjust lower back to more historical trends once the unsustainable trend pops. Some arguments hold very little water in the current landscape. Many markets in the US may be near market bottoms and we will highlight 17 of them. They all have very similar characteristics and some are here in California. Other areas are still over priced by historical measures. Let us examine the markets where price bottoms may have been reached.
17 US markets with potential bottoms
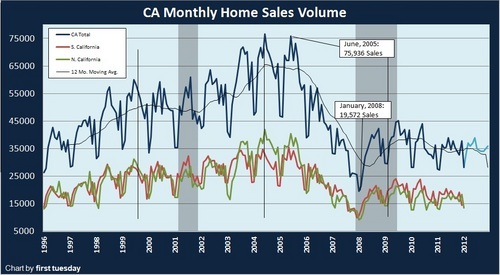
In many markets of the US if you have a solid job buying a house looks to be a good financial move. Yet some people are so niche focus that they forget that the US is much bigger than say Culver City orBurbank. Some may argue that lower interest rates may change the equation but keep in mind low rates apply to the entire country so wouldn’t these income to home price metrics adjust everywhere thus pushing prices up evenly? Of course but this is why some markets may be stabilizing while mid-tier markets in Southern California fell over 5 percent in 2011. Let us take a look at a wide range of markets where home prices may be reaching bottoms:
The list varies across the country. I’ve included a handful of California markets as well. In these areas if you have secure employment and would like to settle down, there is likely to be very little reason not to buy. This isn’t a question of being a bear or a bull. It is a question about understanding home values in a historical and local context.
Home price to area income ratios absolutely matter. You’ll notice one key element here as well. Even with low interest rates a historical home price to income ratio holds steady. Each one of the affordable markets above has a home price to median household income ratio ranging from 2.43 in Bakersfield California to 3.15 in the San Bernardino and Riverside markets here in Southern California. You mean we have some affordable homes here in SoCal? Absolutely. In these markets buying makes sense if:
-You have secure employment-Plan to stay long-term (i.e., 7 years or more)
The cross section above is extremely diverse. You have markets in areas like McAllen and Fort Worth Texas that had almost no bubble even during the craziness of the housing mania. Then you have markets like Pensacola Florida and Merced California that have collapsed so bad that home values are coming back in line with local area incomes.
Where the bubble still roams
The above list includes 11 states and we can include many more as well. The nationwide median home price is close to $150,000 so in many areas, home prices are looking attractive. Los Angeles and Orange counties are not two of those areas.
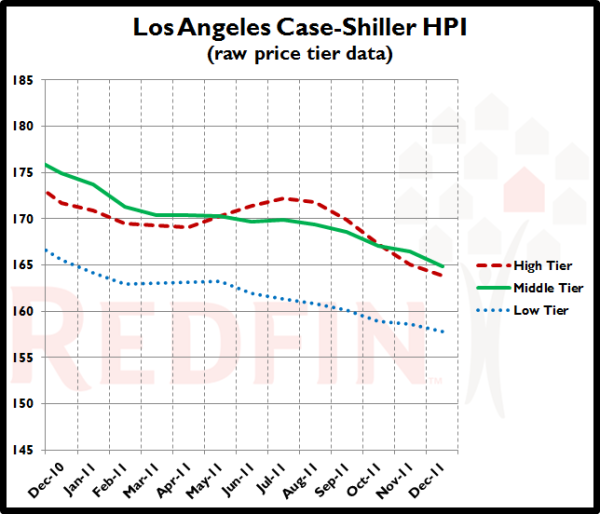
The Los Angeles Case-Shiller data includes Orange County. For the year of 2011 prices continued to move down in these markets:
December 2011 (latest data)Month to Month: Down 1.1%Year to Year: Down 5.2%Prices at this level in: August 2003Peak month: September 2006Change from Peak: Down 40.8% in 63 monthsLow Tier: Under $289,982Mid Tier: $289,982 to $474,017Hi Tier: Over $474,017
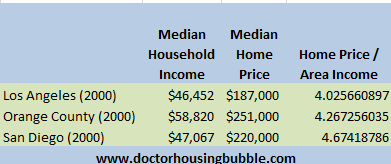
So why are prices still inflated in these markets? Let us go back to 2000 when the bubble was already starting and look at three California counties:
I would argue that the housing bubble in Southern California started in the late 1990s but we’ll be conservative and use 2000 as our baseline. When we look at the metrics above a ratio of 4 seems to hold for home price and income. So compared to our affordable list above, this translates to one more year of household income tacked on to the median home price. As we stated before, low interest rates help the entire nation so why is it that the majority of markets across the country still maintain stable ratios even today while these markets remain inflated? The fact that home prices in mid-tier regions fell over 5 percent in 2011 tells you that yes, home prices in relation to incomes do matter and that is why prices continue to fall.
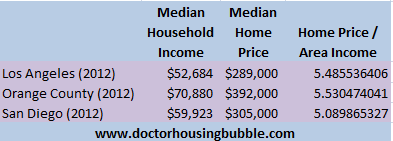
Home prices in these markets today are more inflated than they were in 2000. If we look at incomes and home prices today versus the baseline of 2000 we realize that these markets have gotten more expensive even with prices of today and slightly higher incomes:
Where nationwide it takes roughly 3 years of household income to buy a home, in these three counties in 2000 it took roughly 4 years of household income. Today it is over 5 years of household income and the economy is doing more poorly than it was in 2000:
California unemployment 2000: 5 percentCalifornia unemployment 2012: 10.9 percent
What should you take away from all of this? Home prices in a large cross section of the country look to be affordable. Prices in Los Angeles and Orange counties are still inflated. For home prices in these regions to get back even to their 2000 ratios, prices would need to adjust lower by:
To reach 2000 ratiosLos Angeles: -$78,264Orange County: -$108,480San Diego County: -$65,308
Since most first time home buyers are going in with 3.5 percent FHA insured loans, the above gap is likely to wipe out any down payment. To buy in these counties a tiny amount is needed:
FHA 3.5 percent down paymentLos Angeles: $10,115Orange County: $13,720San Diego: $10,675
Yet some want to get the green light to buy. Look, if you have an absolute need to buy and your life is completely unfulfilled until you buy in one of these mid-tier markets, go ahead. No one is stopping you. In fact, the banking controlled government wants you to overpay. But if you look at this from a purely investment perspective, many other US markets do make sense on every front. For Los Angeles and Orange County mid-tier markets they do not.